Unpredictable difficulties can arise in mechanical and electrical systems. In most cases, a prolonged period of rising heat in the various components of the system precedes the actual failure of the equipment. The issue can be fixed before the electrical equipment fails if the rising heat is discovered in time. When it comes to preventative maintenance, infrared thermography is a useful tool. It can pinpoint places that are abnormally hot or cold. Using technology to investigate electrical issues has some positive outcomes.
In order to avoid the costs resulting out of such incidents, it is crucial to prioritize fire prevention. Electrical thermography is becoming increasingly popular as a supplementary measure to a business’ electrical compliance, which is a crucial aspect of any company’s safety strategy.
What Does Thermography Mean?
Thermography is a passive diagnostic technique used in electrical equipment as a proactive method for identifying faults that could cause future fires and electrical safety issues.
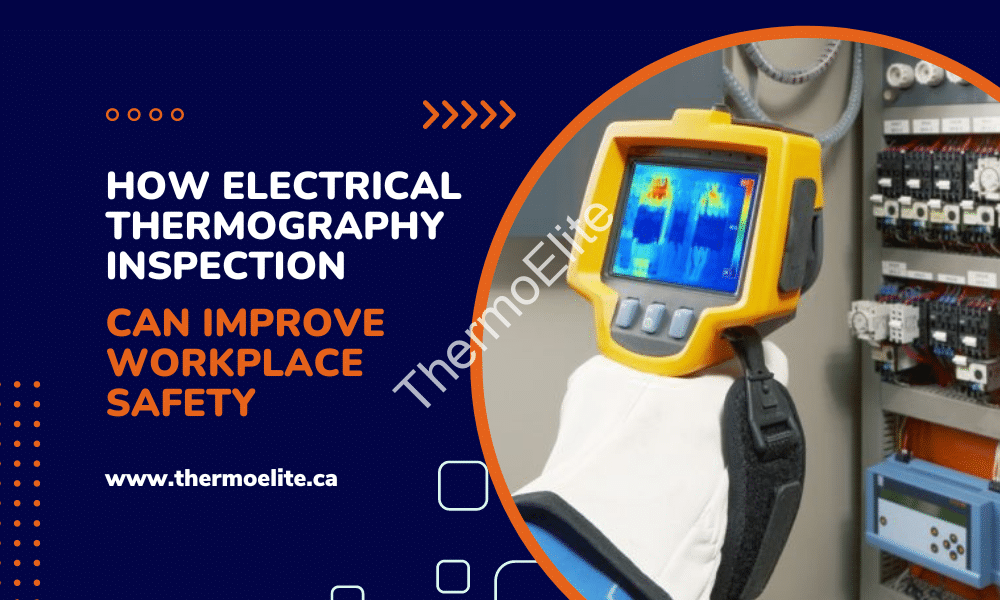
The method is based on the observation that most faulty system components are accompanied by a rise in temperature, and it is used to examine electrical devices by getting heat distribution photographs. It is useful for identifying possible issues in electrical components that are powered, such as hot spots, faulty connections, unbalanced loads, and insulation that has degraded over time.
Thermographic Objective
Hot spots are a good way to locate electrical system problems. Overloading a circuit or having its insulation break down can cause hot spots. Thermography aids in obtaining data while minimizing system disruption.
Breakdowns in the electrical system are expensive and inconvenient. For modern, complicated process systems, maximizing uptime and asset maintenance are essential requirements. A company can suffer permanent damage from even a temporary cessation of output. If a problem is detected via thermography, it can be fixed before a complete breakdown occurs. As a result, we can address it as part of routine upkeep before it becomes an urgent concern.
Why is Electrical Panel Thermography Testing Important?
According to the National Fire Prevention Association, 10% of all fires are caused by problems with electrical systems. These problems might include faulty terminals, insulation, and other electrical components. The Health and Safety at Work Act of 1974, the Electricity at Work Regulations Act of 1989, and BS 7671 (IEE Wiring Rules, 17th Edition, as Amended) all recommend routine inspection and testing of electrical systems.
If you do infrared testing, you will be able to identify issues with the electrical infrastructure while it is under strain throughout the testing process. This is because problem locations will display as having abnormal temperatures in the live image on the thermal imaging device.
What Procedures are Performed During Infrared Thermography Testing of Electrical Panels?
Commercial, manufacturing, and industrial facilities rely on electrical switchgear and panels as the lifeblood for distributing power throughout the facility. Production would halt and money would be lost without it.
Obtaining photographs of the heat distribution in electrical components is one of the goals of testing. This technique relies on the observation that when anything is wrong with a system, its temperature rises. An overheated electrical circuit could be the result of a few things, such as a few loose connections or, in the case of mechanical equipment, a worn bearing. System faults can be discovered and assessed in terms of severity by monitoring the heat patterns generated by functioning system components.
How Are Electrical Panel Thermography Tests Performed?
A thermal imager or infrared camera is used by the inspector as a testing tool. These tools create a thermal image by detecting and analyzing an object’s inherent infrared radiation emissions. Portable thermal imagers with simple controls are available now. Due to the lack of requirement for physical interaction with the system, testing may be conducted with the system fully activated, resulting in zero downtime or production loss.
The Following Pieces of Machinery Should Be Subjected to Frequent Thermography Inspections
- Circuit breakers or fuses
- Distributional Boards
- Busbar apparatus
- Control consoles
- Systems that operate at high and medium voltages
- Insulators and connectors for power lines
- Electrical equipment
- Battery systems and UPS
- PLC connections
- Control centers for motors
- Alternator
- DG Set
Several Problems Can Be Spotted by The Inspection
Infrared thermography can reveal several issues that could reduce the effectiveness of your systems in operation. Overloads, sloppy wiring, inductive heating, short circuits, open circuits, harmonics, imbalanced loads, and broken machinery are all potential causes.
Safety
A sudden breakdown might result in dangerous situations because of how quickly complicated industrial systems operate. There is a risk that your employees will be injured by flying objects. The instrument assists in preventing fires brought on by circuit overloads or bad wiring through early detection of electrical issues.
Economic Benefits
Problems can be found and fixed with the use of infrared thermography inspections. As a result, there will be fewer downtimes and disruptions overall. Early detection and repair of malfunctioning machinery results in not just increased output but also substantial cost savings.
Excellence
Most of the time, reliable and consistent processes are what produce quality. All systems will function at their best after electrical issues have been resolved. As a result, you’ll be able to provide customers with high-quality goods, which will increase your brand’s credibility and sales.
Cheaper Premiums for Insurance
Fewer disruptions mean less downtime for your company, which in turn means better profits and more money coming in. If you have business interruption insurance, your rates will be cheaper.
In today’s era of electrical equipment upkeep, worker safety has become the top priority. The days of crossing one’s fingers and donning protective gear are over. During operation, electrical components can be inspected for problems such as loose connections, unbalanced loads, deteriorated insulation, and more with the help of a passive testing method called thermography. Excessive energy consumption, high maintenance costs, or catastrophic equipment failure can lead to unanticipated service interruptions, damaged equipment, and other problems.


Add Comment