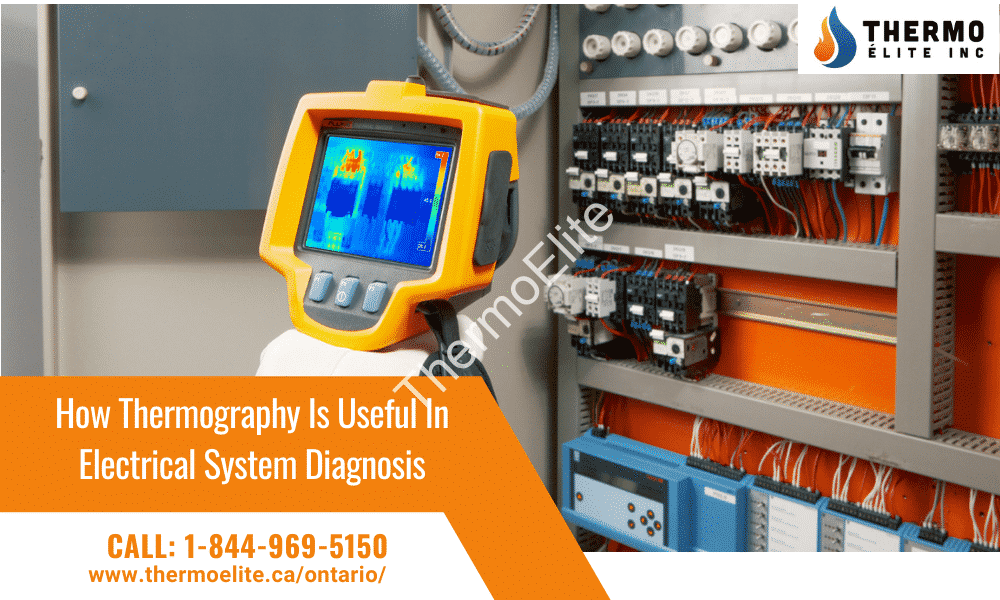
As a method of non-destructive testing, thermography is very useful in detecting poor connections, load imbalance, poor insulation, or other potentially risky issues in electrical systems. If these issues persist, you end up with higher power use and maintenance costs. If you neglect the repair and maintenance of faulty electrical systems, it might lead to graver consequences. These will eventually lead to unscheduled interruptions in service or serious equipment damage. Let’s understand how thermography helps in the early diagnosis of faults in electrical systems and prevent major accidents.
How to use thermography for electrical instruments inspection
Faulty electrical systems are in the energized state thereby radiating heat, which is the result of the electrical resistance. The amount of heat generated depends on the total current flowing through the system. It’s also decided by how strong the resistance of separate components and connections in the system is. When there’s deterioration in the components, there’s an increase in their resistance, which triggers localized heat generation. A poor connection shows a higher resistance than strong connections, which causes it to have a higher heat signature. Thermography helps you detect these temperature differences.
How thermography works
Thermography, also referred to as infrared inspection, works by detecting infrared radiation caused by the heat that the surface of any component emits when there’s any fault in it. Infrared cameras are used to detect such heat emissions. The cameras have inbuilt software to convert the infrared radiation they capture into a thermal image which is presented in a report showing the component’s thermal condition during the test. The report thus presented is a representation of heat being emitted, which indicates a fault in any component of an electrical system.
The usefulness of thermography
A National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) estimate says that electrical system failures cause ten percent of the fires in manufacturing facilities. These failures exist in the electrical insulation, the terminals, and other related components. Faulty electrical systems may expose employees to live electrical circuits that can cause serious injuries or fatalities by electrocution. Timely detection of connections showing high resistance during thermography followed by necessary repairs reduces the likelihood of any breakdown in the wires or any components. They help in carrying out effective preventive maintenance.
There are other advantages of timely detection and repair of faults in electrical systems. You conserve energy and save costs. Timely maintenance prevents expensive repairs and outages caused due to unexpected interruptions. There’s an increase in current flow when the resistance in circuits is high. Higher current flow results in more power consumption giving you inflated bills. Again, if the current draw is high, critical components in an electrical system like fuses, circuit breakers, or transformers may suffer premature failure. Such failures trigger higher costs of maintenance and repairs or interruptions in business – all of which can be prevented with timely detection of faults through thermography.
When is thermography necessary?
Thermography can benefit all properties. However, for those where the power consumption is high, where multiple branch circuits and distribution subsystems, or heavy equipment is present, the need is critical. Businesses, where electricity consumption is high, should conduct thermographic scans on critical systems like circuit panels, switchgear, and transformers at least once a year. The scan results should decide a schedule for rescanning based on the equipment types, rate of power consumption, and total usage time of an electrical system. A qualified electrician should be approached to determine what to scan and how often to scan.
The NFPA published NFPA 70B, Recommended Practice for Electrical Equipment Maintenance provides in its Annex L, a list mentioning intervals in equipment testing for maintenance. Apart from the intervals mentioned, there may be a need for more frequent inspections under certain circumstances and conditions, which include-
Power systems and equipment
- Aluminum wiring in buildings
- Motors with high torque and heavy current draw
- Modifications to be carried out in electrical panels, power control boxes, and sub-panels
- Motor starter circuits
- Power systems that have electrical services of more than 120 volts
- Switchgears, relays, and other power transfer circuits
- High output lighting equipment being present, such as mercury vapor
- Presence of step-up and step-down power transformers
- Uninterrupted power supply being used
Observations
- There is a rise in power consumption despite no rise in equipment usage
- Lights getting dim when other equipment is started
- Temperature changes in electrical equipment
- A slowing down of computers, motors, and other equipment being reported
- An inexplicable odor of plastic or rubber burning where electrical panels, wiring, or equipment are located can’t be explained
- An unexplained surge in power was observed in computers or building service equipment
Property history
- Construction or repair activities causing higher demand for electricity
- Previous instances of fires in electrical systems
- Previous instances of frequent bulb changes or fluorescent lights failing
- Damage caused to facilities by fire or natural disasters
Some tips for useful and effective thermal imaging
Stable environmental conditions are necessary for proper thermography. The outside temperature and other factors like wind should not fluctuate frequently. A thermographer should ensure the following conditions and take these steps before commencing the test:
- No direct sunlight
- No presence of wind or air currents
- The use of a stand to place the thermal camera on for higher operator safety and better measurements
- Images should be taken from various angles to evaluate what effect reflections might have on the thermal images taken
Conclusion
Thermography, therefore, helps in the proper and timely detection of faults in electrical systems by locating higher temperatures in components, a result of higher resistance caused by the faults. Such timely detection of faults in electrical systems helps prevent major outages that cause downtime and loss of man-days. Undertaking timely repairs boost the safety of workers ensuring that there are no fires or other accidents like electrocution. Thermography helps design a proper preventive maintenance program that ensures that all electrical systems give optimum performance.