Thermography has recently emerged as the most preferred method for testing electrical panels as it can accurately detect unbalanced loads, poor connections, damaged insulation, or any other problems. The electric panel is an energized electrical component that results in excessive power usage, higher maintenance costs, or complete failure of the equipment leading to permanent equipment damage, unscheduled service interruptions, or other issues.
What’s the Science behind Thermography?
Infrared inspection or thermography is a technology based on heat sensing usually emitted from various objects’ surfaces. Detection of this infrared radiation forms the basis of thermography. Various tools are used to detect and convert the infrared radiation into a thermal image or temperature value that is used to analyze later and assess the object’s thermal condition when the measurement was taken.
An infrared camera is one of the more popular thermal imaging devices used frequently for thermographic inspections of electrical systems.
Importance of Thermographic Testing Of Electrical Panel
According to the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), out of all the fire disasters, 10% of them can be attributed to electrical systems failure, including faulty terminals, leakage in electrical insulation, and other faulty electrical components. Specific guidelines on the regular compliance and maintenance of electrical infrastructure are mentioned in the Electricity at Work Regulations Act 1989, Health & Safety at Work Act 1974, and BS 7671.
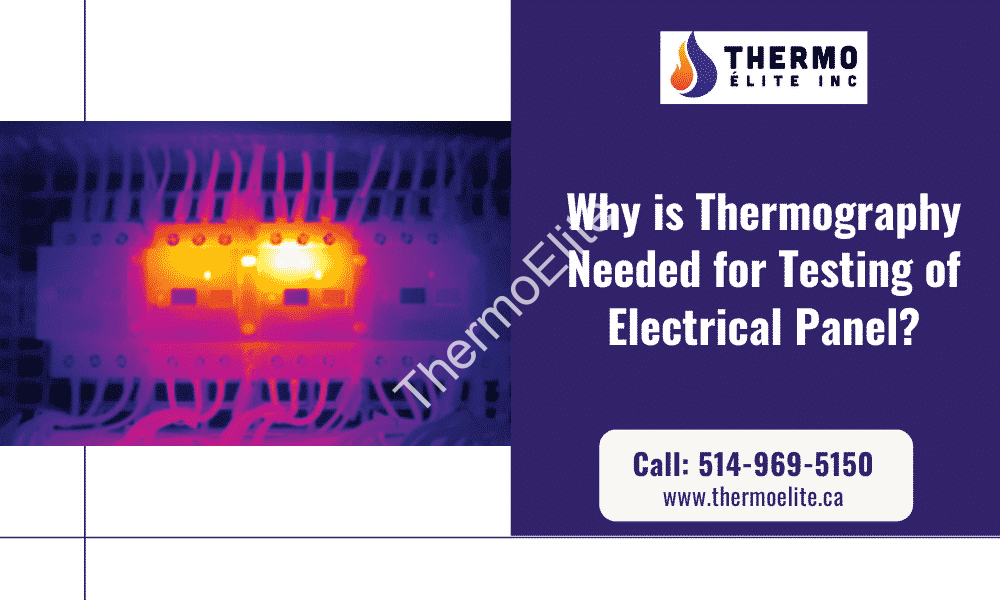
Infrared inspections of electrical systems under load will display anomalous temperatures, easily captured by thermal imaging cameras. Faulty electrical systems or wiring can expose employees to live circuits, resulting in electrocution injuries or death. Thermal imaging cameras can easily detect the high-resistance sections. Once the problems are detected, pre-emptive maintenance and repair work can be undertaken to prevent the unnecessary breakdown of electrical systems or components.
Other obvious benefits of detecting faults in the electrical panel and preemptive repair include the financial benefits realized through energy conservation, prevention of unnecessary breakdowns, and reduced repair charges. Whenever a circuit or electrical component experiences high resistance, there will be an increase in the current flow, leading to higher power consumption. An increased current draw will eventually lead to premature collapse or damage of fuses, circuit breakers, and transformers.
As we all know, the failure of electrical panels leads to higher repair and maintenance costs and interruptions in business operations.
Prominent benefits of Thermography Testing of Electrical Panel
- Assesses proper installation or maintenance of electrical systems or components
- Cuts downtime
- Brings down the frequency of equipment failure
- Enhances safety
- Improves the chances of insurance coverage
- Enhances system performance
- Helps in finding out whether the electrical systems or components are working correctly or not
- Determines whether the electrical systems comply with the project design and specifications
- Cuts down delays in the construction schedule
- Save money
How is the Thermographic Inspection of Electrical Panels Carried Out?
Thermographic inspection of the electric panel is a highly-professional task carried out by trained thermographers. Since the entire thermography process is non-invasive, the inspection can be carried out while the electrical system or components are operational. Another great thing about the thermographic inspection is that it can be carried out without any risks of injuries to the thermographer or maintenance staff.
Electrical panels and switchgear control the entire supply of electricity to industrial, manufacturing, and commercial buildings. Production will come to a grinding halt in the absence of electricity resulting in substantial financial losses. An infrared inspection is a useful tool for detecting electrical problems, thereby allowing the maintenance and repair team to undertake preemptive steps and prevent dangerous and expensive electrical outages.
The heat distribution images captured during the infrared thermographic inspection of electrical components can help thermographers pinpoint the sections experiencing problems. The testing is based on the simple scientific principle of heat sensing. The electrical panels that show an increased temperature is facing issues and have to be repaired or replaced. The malfunctioning of electrical panels increases the resistance, which in turn leads to overheating of the components. Now, the heat patterns captured by an infrared tool can be analyzed to assess the electrical panel’s exact condition, and the faults can be detected. The thermographic images analysis is essential to understanding the level of damage or seriousness of the issue plaguing the electrical panel. Preemptive maintenance tasks can be undertaken quickly wherein the faulty component can either be repaired or replaced.
What’s the Role of a Certified Thermographer?
Certified thermographers are well-trained and qualified professionals who can carry out complete thermographic inspection of industrial, commercial, manufacturing facilities, power plants, utility substations, schools and colleges, maritime vessels, data centers, hospitals, medical facilities, water treatment facilities, etc. they have the necessary skills and experience to handle a variety of issues plaguing electrical panels or systems.
The thermographer or inspector uses an infrared camera or thermal imaging device to test electrical panels. The infrared cameras are used to capture natural infrared radiation from the heated electrical component and produce thermal images that can be analyzed using software applications for heat anomalies. The inspector will never ask the facility owner to switch off or halt operations during the testing, as thermography is a non-invasive procedure. It can be done when the electrical panel is in an energized state. Thus, there’s no production loss or downtime when the inspector carries out the electrical panel’s thermographic test.
Some of the Issues That Can Be Detected by Thermal Testing
- Connections exhibiting high resistance
- Hot spots
- Overloaded cables
- Overloaded fuses or breakers
- Conveyor or motor experiencing failures
- Overheating of motor windings
- Distribution equipment overheating
- Phase load imbalance
- Overheating of overcrowded trunking
- Thermal loss
- Breakdown of Thermal insulation
- Damp ingress
Steps Followed During an Electrical Panel’s Thermographic Testing
- The electric panel should be energized and provided with adequate load before testing as all components need to be tested under average operating load.
- The electric panel being tested must be examined thoroughly before removing or opening any cover to determine the possibilities of unsafe conditions.
- If the electric panels show unusual heating or the condition is beyond normal, the thermographer and a team of specialists can take appropriate measures before starting with the thermographic inspection.
- All the lids and enclosures must be opened so that visual access to all the electrical panel components is available to the inspector. If further disassembly is needed, then it must be granted for better-infrared inspection.
- To get clear thermographic images, the panel being inspected should be adequately accessed, and the maintenance team must ensure this.
- Thermographic inspection can either be quantitative or qualitative, depending n the preferences of the inspection team.
- Even during quantitative testing, the inspector must use a thermal imaging camera instead of the imaging radiometer. The infrared imaging camera’s resolution must be good enough to produce clear images of the electrical panel.
- During the process of infrared testing, the thermographer must ensure that all the non-contact temperature readings are accurate enough.
- Similar components using a similar load must be compared for every reading.
- The electrical components that show temperature anomaly or abnormal thermal patterns should be reported along with thermal images or excluded after a thorough analysis of the images.
- Thermal images and readings must be saved in secure storage to be used for future reference.
- Daylight cameras equipped with thermal imaging tools must be used to capture appropriate images of the electrical panel.
- Thermographers must ensure that the captured images are visible enough to reveal all the details.
- The thermographer must pay attention to factors like focus, resolution, lighting, and contrast.
- It’s essential to include both the visible as well as the thermal images.
Necessary Documentation for Report Preparation
- Distance between the thermal imaging camera to the electric panel or component
- Include the details of the maximum rated load of the component and the load measured when tested
- It’s essential to take into account the surface temperature of the electrical panel and the standard temperature
- If needed, the evaluation of temperature severity of the electric panel must be taken
Detailed documentation must be prepared to include all the faulty components with higher repair priority depending upon their temperature severity


Add Comment